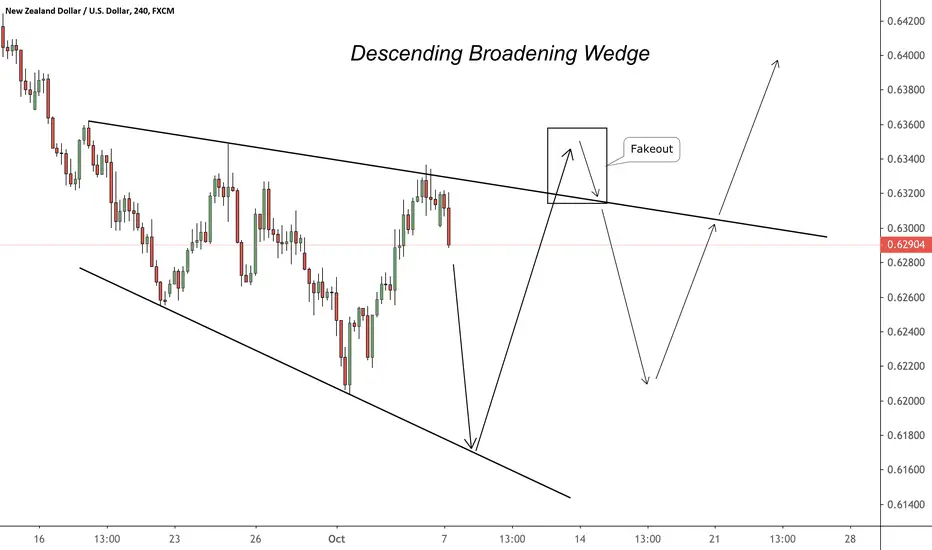
A descending broadening wedge is a bullish chart pattern that is considered a reversal pattern. This pattern is formed by two diverging bullish lines, with the upper line acting as resistance and the lower line as support. To confirm a descending broadening wedge, there should be good oscillation between the two upward lines, with each line being touched at least twice to validate the pattern. This pattern indicates the buyers’ ambition to take control rather than marking the exhaustion of the selling current. The divergence of the two lines in the same direction informs that the price continues to fall with movements of decreasing magnitude. The descending broadening wedge typically leads to a bullish reversal after a trough or during a correction in a bullish movement.
what are other reversal patterns in technical analysis
Other reversal patterns in technical analysis include:
- Double Tops and Bottoms: Double tops occur at the end of an uptrend when the price reaches a resistance level twice without breaking it, indicating a potential reversal. Double bottoms, on the other hand, form at the end of a downtrend when the price hits a support level twice without breaking it, signaling a possible reversal4.
- Head and Shoulders: This pattern is recognized by three peaks, with the middle peak (head) being higher than the other two (shoulders). In a bullish trend, this pattern suggests a potential reversal when the price breaks below the “neckline” connecting the lows of the two shoulders. In a bearish trend, an inverse head and shoulders pattern can indicate a potential reversal4.
- Quasimodo Pattern: The Quasimodo pattern is relatively new but powerful for identifying reversal opportunities. It occurs after a significant uptrend or downtrend. In an uptrend, it shows a shift from bullish to bearish momentum, while in a downtrend, it indicates a change from bearish to bullish momentum. The entry point is typically at the last peak or bottom before the reversal.
how to use support and resistance levels to identify potential reversals
Support and resistance levels are crucial tools in technical analysis for identifying potential reversals in the market. Here’s how you can use them effectively:
- Support and Resistance Basics: Support levels act as a floor under the price, preventing it from falling further, while resistance levels act as a ceiling above the price, preventing it from rising further24.
- Identifying Support and Resistance Levels: Traders look for areas where the price has historically bounced or reversed, indicating strong buying or selling pressure. These levels can be horizontal, diagonal (trendlines), round numbers, Fibonacci retracements, extensions, or pivot points345.
- Role Reversal: When a price breaks through a support or resistance level, it can signal a potential reversal. A broken support level can become a new resistance level, and vice versa. This shift in supply and demand dynamics indicates a change in market sentiment45.
- Confirmation: It’s essential to confirm a potential reversal using additional indicators like volume, candlestick patterns, or other technical tools. A single breakout may not be sufficient to confirm a reversal, so looking for multiple signals can strengthen the analysis5.
- Market Psychology: Support and resistance levels are influenced by market psychology and behavioral finance. Traders often anchor to these levels, considering them as significant points for potential reversals. Round numbers and key technical levels can act as psychological anchors for traders25.
By combining the identification of key support and resistance levels with confirmation signals and an understanding of market psychology, traders can effectively use these levels to anticipate and capitalize on potential reversals in the market.